Acute stroke care
from symptom-onset to specialized therapy via rescue and hospital network
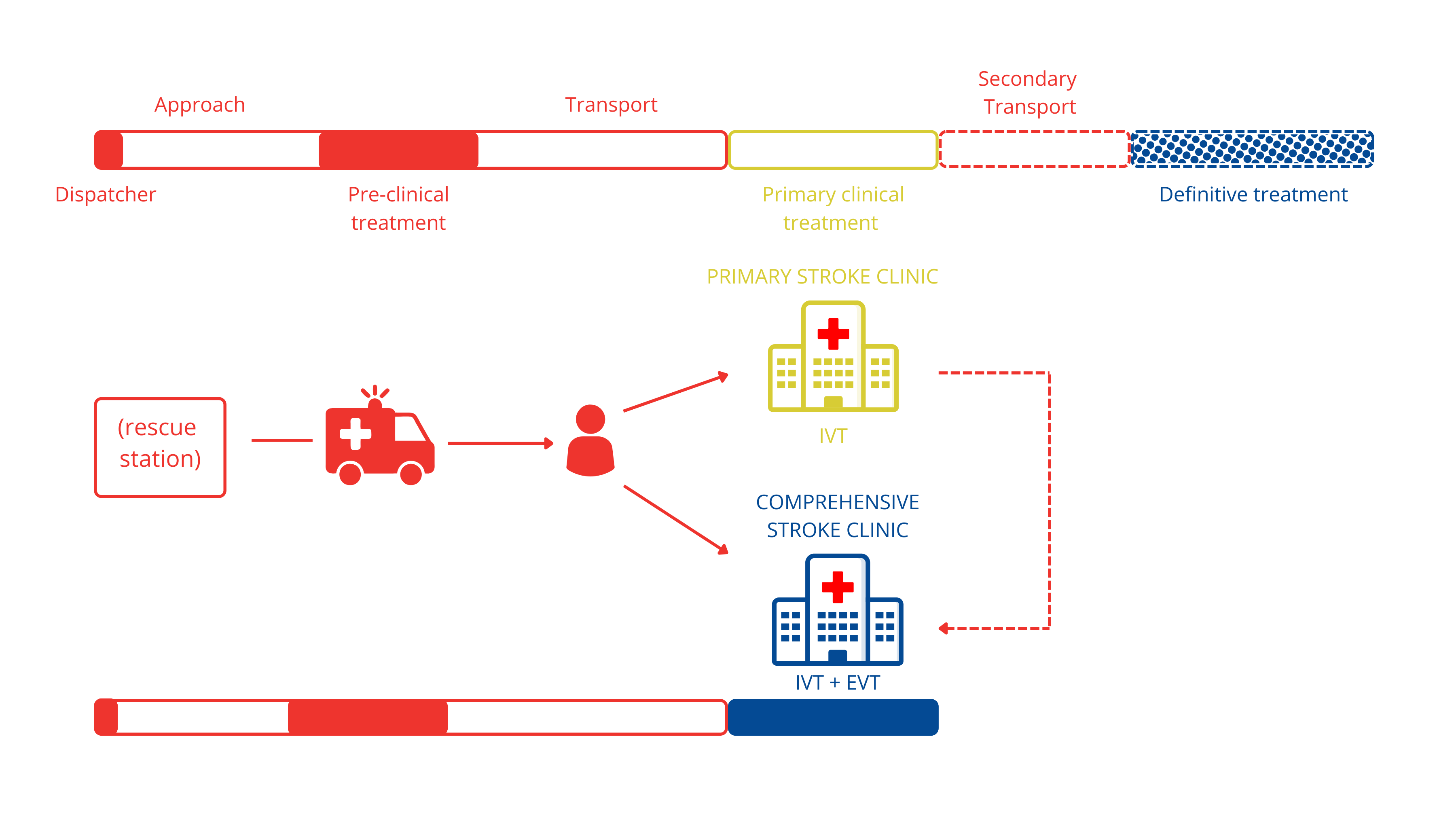
from symptom-onset to specialized therapy via rescue and hospital network
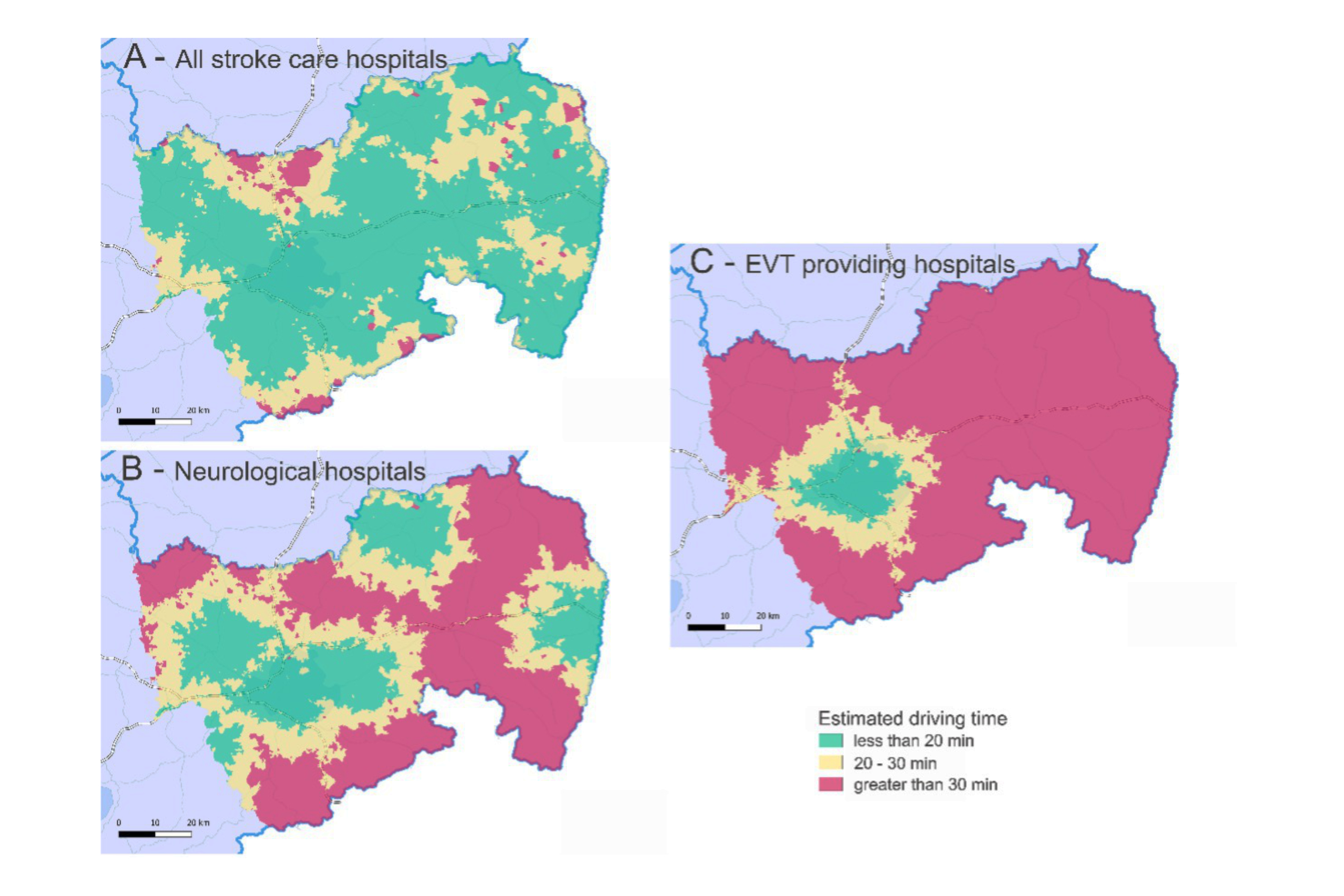
Travel time considering a maximum of 30 minutes according to DSG recommendation to the nearest center
The ARAS project focuses on improving acute stroke care by developing a decision-support algorithm that optimizes patient allocation. In Eastern Saxony, stroke is a leading cause of death and disability, with a population that faces challenges due to sparse hospital coverage and limited resources. Inefficient allocation of patients often results in delayed treatment, higher mortality rates, worse clinical outcomes, and increased economic costs. The project will analyze current transport pathways using simulation tools, incorporating real-world data on preclinical patient status, transportation duration, and hospital treatment capacities. These simulations will reveal inefficiencies in the existing system and help model optimized allocation strategies.
The core outcome of ARAS is an algorithm that supports first responders in selecting the most appropriate hospital for each patient based on transport times and available treatment options, such as CT imaging, endovascular therapies, and specialized care units. A web-based prototype will be developed to provide real-time, transparent recommendations. Additionally, ARAS will evaluate the economic impact of optimized resource allocation, addressing treatment delays, unnecessary transfers, and limited rescue service availability. The project not only aims to enhance the efficiency of acute stroke care but also to improve overall patient outcomes, particularly in aging and underserved regions.
Future potential includes scaling the algorithm for broader regional applications, such as neighboring states, and adapting it for other medical emergencies like heart attacks or trauma care. The project will serve as a foundation for advanced machine-learning tools and further clinical studies, contributing to sustainable and optimized healthcare delivery in emergency scenarios.