A donor/recipient on chip device for automated, cell-based crossmatch to expand survival of living kidney transplants |
Medical Need
In Germany, approximately 85,000 people require permanent renal replacement therapy caused by chronic renal insufficiency. Kidney transplantation (KTX) is the therapy of choice because quality of life and life expectancy are fare better than in dialysis therapy. There are more than 12,000 patients on the waiting list for KTX in Germany. In 2018, 37 transplant centers have transplanted a total of 2,291 kidneys. With 638 kidney transplants after living donation. Nevertheless Antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) after KTX is the major limitation for long term survival of the donated kidney within the recipient allograft. It is caused by cell-mediated immune response and thus cannot be detected by HLA crossmatch testing alone.
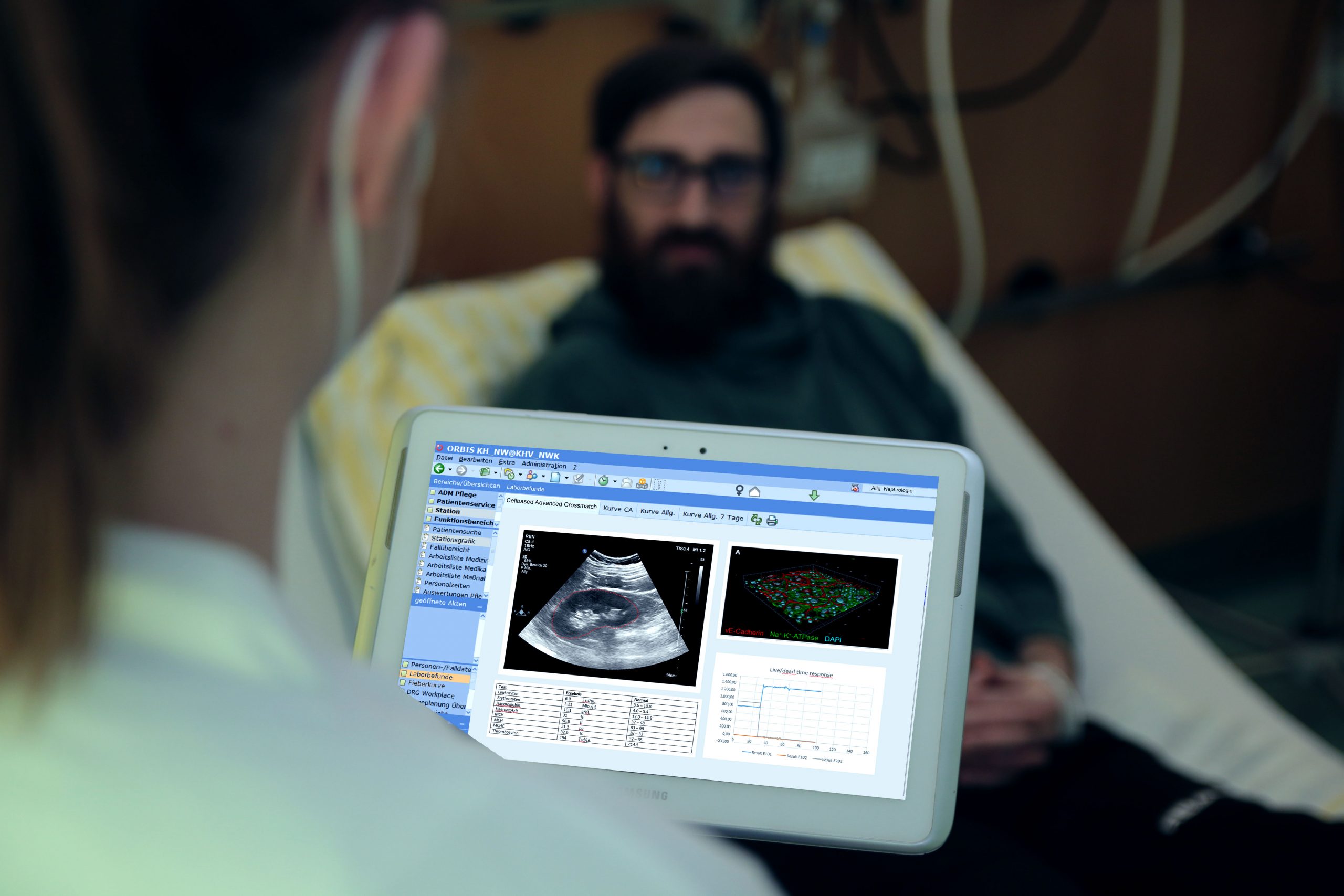
This project will address the issue of antibody mediated rejection by supporting the clinician with additional information about the donor specific immune response of the recipient. We are going to demonstrate that novel additional cell based in vitro tests can gain further information that will help to estimate and increase the survival of the transplant, virtually bedside.
kidney transplantation (KTX), Antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR), connected care, advanced crossmatch
Abstract |
This project will address the issue of Antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) after kidney transplantation (KTX) as the major issue of organ rejection. Therefore the project team will develop an automated cell culture device, a corresponding assay to test for the occurrence of ABMR in vitro bevor KTX and implement a data pipeline to integrate the assay data into Laboratory Information and Management System (LIMS) and Clinical Information System (CIS). Therefore, a microfluidic device, and protocols to cultivate specific cells of donor and recipient within that device should be developed in the project. Furthermore, cellular response will be tracked by several automated readout methods. The readout devices will be implemented into the (LIMS) to directly connect data of the assay with the involved clinicians via CIS. Thus it not only provides extra information to existing tests, like HLA crossmatching, but additionally helps the doctor to quickly estimate the probability of ABMR on the basis of a laboratory test, virtually bedside.

